The Additive Manufacturing process - Building an object layer by layer. (Source: Cyant)
Additive Manufacturing is the process of creating a three-dimensional (3D) object by adding one layer of material on to another layer until a full object is created. The main difference between additive and traditional manufacturing methods is based on how objects are made. During traditional manufacturing, materials are often molded, removed or carved out, but during additive manufacturing, materials are only ever added.
Most 3D printers are a form of additive manufacturing, but some use different additive methods to create 3D objects. Examples of different 3D printing processes include; Fuse Deposition Modeling (FDM), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Stereolithographic Apparatus (SLA).
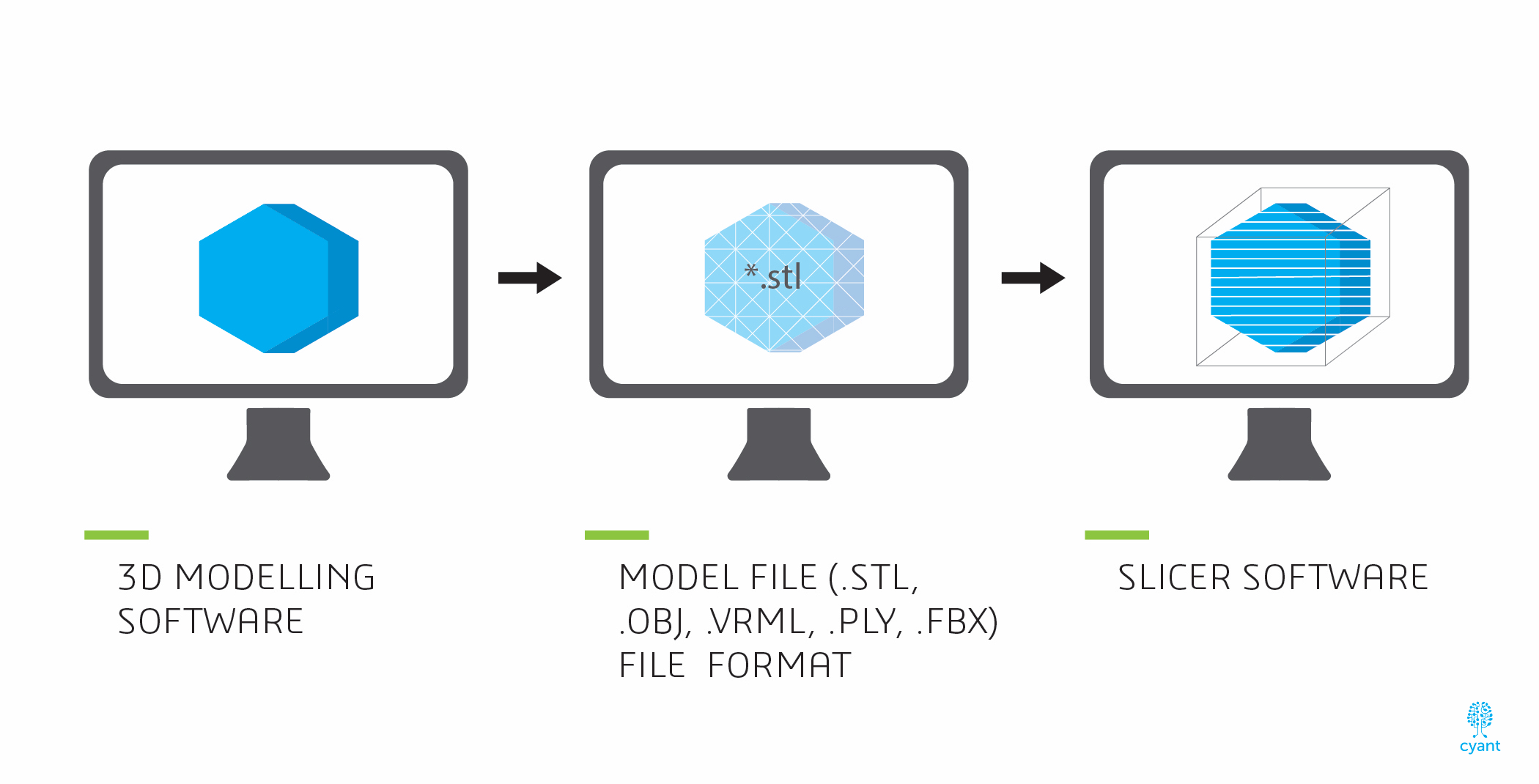
From 3D modeling to 3D printing - Part 1/2. (Source: Cyant)
Despite being different 3D printing processes, they all follow a similar set of steps to create 3D printed objects. First, a 3D modeling program (such as Cyant’s Lab) is used to create a 3D computer model. The computer model is then saved in a file that describes the geometry of the model. A typical format for this file is the STL file format.
From 3D modeling to 3D printing Part 2/2. (Source: Cyant)
The model file is then opened in a slicer software, where the model is “sliced” into the individual layers that will be printed. The slicer software also collects information from the model file and creates a G-code. This code instructs the 3D printer on how to print the 3D object- one layer at a time- by controlling the speed, movement, height and path of the 3D printing machine. Together these processes bring your 3D models to life!
A complex 3D printed object. (Source: Brewbooks from near Seattle, USA)
3D Printing enables the creation of parts and objects that cannot be produced with traditional methods. This means new things can now be designed and this makes this technology very exciting. Still, 3D Printing can also be used with traditional crafts. So beautifully designed objects can be created from the combination of time-proven techniques and new technologies!